Supply Chain Resources
Useful links
Our transportation and supply chain resources are here to help you better navigate the ever-changing and dynamic world of global shipping. Saving you time and allowing you to focus on your business is what we’re here for. Below are some links we have gathered that we find useful in our daily operations, and you might, too.
Incoterms
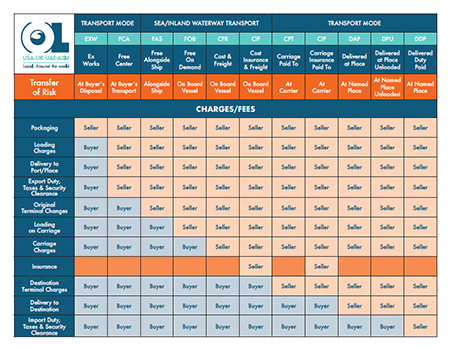
What are Incoterms®?
Incoterms define the level of risk within the international shipping process. Outlining where the responsibility and costs for cargo transfers between sellers (shippers) and buyers (consignees).